An interactive journey through the history of Jazz
The Jazz History Tree is designed to provide a fun, educational, digital, and interactive trip through the history of over 30 genres of Black American music from their origins to today. Explore the roots, the creators, and enjoy the music and videos of the masters…..from the blues to rag time, to rock and roll, to hip hop to today. Skim through the interactive Jazz History Tree in a few minutes or explore in detail over days, weeks or months. We invite you to explore the birth and growth of this spiritual art form through the Jazz History Tree.
An interactive journey through the history of Jazz
“The Jazz History Tree is designed to provide a fun, educational, digital, and interactive trip through Jazz History from its African American origins to today. Explore the roots, the creators, and enjoy the music and videos of over 30 genres …..from the blues to rag time, to rock and roll, to hip hop to today. Skim through the interactive Jazz History Tree in a few minutes or explore in detail. We invite you to explore the birth and growth of this spiritual art form through the Jazz History Tree.
Just click the genre cards below and begin your journey.
JUST CLICK THE GENRE CARDS BELOW THE TREE AND BEGIN YOUR JOURNEY
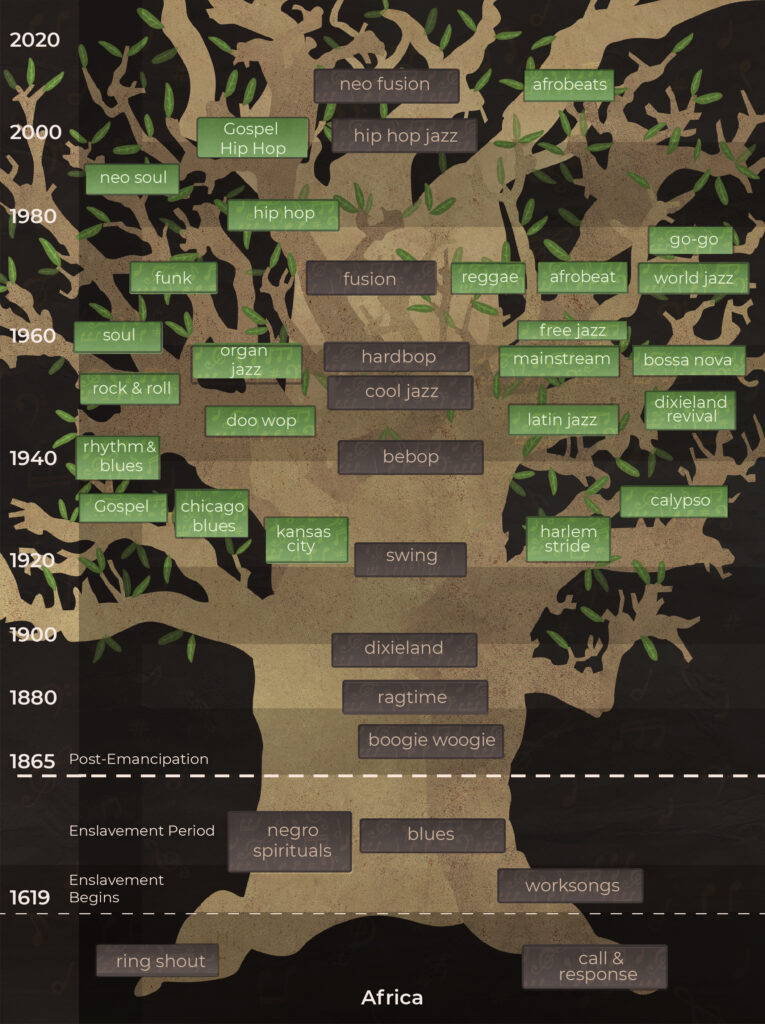

Jazz was created in America by African Americans but draws from the ancient African cultural traditions of call and response and ring
shout.

While the European musical tradition emphasizes performing patterned music written by others, the African musical tradition incorporates improvisation and the nuanced and explosive call and response, or participation, as a basis for powerful human expression. …Read More

The ring shout is a spiritual expression in dance. It has its origins in a dance form, indigenous to much of Central and West Africa, in which the dancers move in a counterclockwise circle. …Read More

African American work songs originally developed in the era of slavery, between the seventeenth and nineteenth centuries. Because they were part of an almost entirely oral culture, they had no fixed form and only began …Read More

Fisk Jubilee Singers
African American (Negro) spirituals emerged from a mix of the brutal institution of slavery, Christian influences, and African culture. The songs expressed a yearning for a better life, claimed identification with the children of Israel, …Read More

The African influence in the blues is undeniable. The poetic structure and story-like verses carry on the oral tradition of West African cultures. Many African cultures made and performed on instruments similar to what …Read More

Boogie-woogie is a style of blues music, usually played on the piano, that is closely related to jazz forms such as ragtime and stride piano. As time went on, solo boogie-woogie extended from …Read More

Ragtime is a musical style that enjoyed its peak popularity between 1895 and 1918. Its cardinal trait is a syncopated or “ragged” rhythm.1 Sometimes referred to as “jig piano” or “piano thumping,” ragtime originated in …Read More

Dixieland, also known as hot jazz or traditional jazz, is a style of jazz developed in New Orleans at the start of the twentieth century. The rhythms and variations played in the city’s Congo Square …Read More

Swing is a style of jazz that, unlike Dixieland, features a larger-than-usual big band and a smoother beat, with flowing phrasing and less complex rhythms and harmonies than those featured in modern jazz.

Commonly referred to as stride, Harlem stride piano is a style of jazz piano that is a derivative form of Kansas City jazz and an extension of ragtime. According to historian Mervyn Cooke in his book Jazz, …Read More

Kansas City is world-renowned for its rich jazz and blues legacy. Blues formed the basic vocabulary for KC-style jazz. Blues singers of the 1920s and ragtime music greatly influenced the music scene, …Read More

Indigenous to Chicago, Illinois, Chicago blues is an electric blues style of urban blues. Urban blues evolved from classic blues following the Great Migration of African Americans, which was both forced and voluntary at times, …Read More

The calypso in Trinidad and Tobago is mainly of African origin and can be traced to the traditions of West Africa. The African traditions of call and response and ring shout are clearly present in calypso. …Read More

Deeply rooted in the rich traditions of Negro Spirituals and the African-American church. Gospel Music took form through the 1920s and emerged in the 1930s, propelled in part by the “great migration” of African Americans
…Read More

Many consider the birth of bebop in the 1940s the beginning of “modern” jazz. Bebop developed as the younger generation of jazz musicians expanded the creative possibilities of jazz beyond the dance-oriented swing style. …Read More

Rhythm and blues (R & B) was the most popular music created by and for African Americans between the end of World War II and the early 1960s. Georgia artists such as Ray Charles, Little Richard …Read More

Doo-wop is a subcategory that focuses on vocal jazz. This includes group harmony, a wide range of vocal parts, scat-like syllables, light or no instrumentation, and R & B rhythms and lyrics. The term doo-wop …Read More

Afro-Cuban jazz is the earliest form of Latin jazz. It mixes Afro-Cuban clave-based rhythms with jazz harmonies and techniques of improvisation. Afro-Cuban jazz emerged in New York City in 1947 with …Read More

Big bands overshadowed Dixieland in the 1930s, but by the early 1940s, there was a revival of “Dixieland” music harkening back to the original New Orleans/Dixieland style. This was driven largely by record company reissues …Read More

Originally called “race music” because of its African American origins, rock and roll is a form of popular music that emerged in the United States in the late 1940s and early ’50s. Fats Domino was …Read More

A style of modern jazz that emerged in the US after World War II, cool jazz was created in contrast to the bebop movement and is more laid-back, featuring slow or moderate tempos and formal …Read More

Hard bop is an extension of bebop. The term “hard bop,” which emerged in the 1950s, was used to describe the new take on jazz that incorporated elements of rhythm and blues, gospel, and blues. …Read More

Bossa nova is a musical sub-genre derived from samba, with strong American jazz influences. Samba is a Brazilian music genre and dance style, with its roots in Africa (via the West African slave trade) …Read More

“Mainstream jazz” is a term established in the 1950s by music journalist Stanley Dance, who considered anything within the popular jazz music of the swing era “mainstream.” Another way to describe mainstream jazz is music …Read More

In a jazz context, an organ trio is a group of three jazz musicians, typically consisting of a Hammond organ player, a drummer, and either a jazz guitarist or a saxophone player. In some cases, …Read More

Soul music was partially the result of the urbanization and commercialization of rhythm and blues in the 1960s. Young black musicians, often nurtured in black churches, enjoyed and listened to …Read More

Free Jazz emerged during the late 1950s, reached its height in the ’60s, and has remained a major development in jazz since. There are no rules in Free Jazz. Musicians do not adhere to a fixed …Read More

Reggae is a genre that was strongly influenced by American jazz and R & B, especially the New Orleans R & B practiced by Fats Domino and Allen Toussaint. Reggae evolved out of the earlier genres ska and rocksteady. ..Read More

Ethno jazz, also known as world jazz, is a sub-genre developed internationally in the 1950s and ’60s broadly characterized by a combination of traditional jazz and non-Western musical elements.1 Jazz had become so popular …Read More

Jazz fusion is a musical genre that developed in the late 1960s when musicians combined jazz harmony and improvisation with funk, rock and roll, and R & B. The electric guitars, amplifiers, and keyboards that were popular …Read More

Funk is a music genre that originated in African American communities in the mid-1960s when African American musicians created a rhythmic, danceable new form of music through a mixture of soul, bebop/hard bop, and R & B. …Read More

The musical genre Afrobeat originated in the 1960s and 1970s as a blend of traditional Yoruba music with jazz …Read More

In the early 1970s, Washington, D.C.-based musical pioneer Chuck Brown began laying the foundation for a new and innovative sound called go-go music. Driven by teenage musicians and audience members, the music was heavily …Read More

Said to be coined by Grandmaster Flash and the Furious Five member Keith “Cowboy” Wiggins, the music movement of hip-hop can be traced back to a “burnt out” South Bronx in New York City …Read More

Neo soul is a musical genre that fuses contemporary R & B and soul with elements of hip-hop, gospel, and jazz. Neo soul music is essentially modern-day soul music with contemporary attitudes and sensibilities. …Read More

Emerging in 2000, the musical convergence of hip-hop and jazz was inevitable. After all, early gospel, blues, and jazz employed call-and-response cadences dealing with the same themes prevalent in hip-hop: procreation, braggadocio, …Read More

In the late 1990s, Gospel Hip Hop was ignited essentially by Kirk Franklin’s chart-topping album God’s Property from Kirk Franklin’s Nu Nation in 1997. At the time of its release… Read More

Afrobeats sometimes referred to as Afro-pop and Afro-fusion is vibrant dance music that draws on West African rhythms and mixes them with genres from across the Americas …Read More

Neo fusion is a term I am coining to describe what I believe to be a new genre of jazz emerging in the 2010s. I admit I’m out on a limb in the sense that …Read More

Just click the genre cards below and begin your journey.
Jazz was created in America by African Americans but draws from the ancient African cultural traditions of call and response and ring
shout.
While the European musical tradition emphasizes performing patterned music written by others, the African musical tradition incorporates improvisation and the nuanced and explosive call and response, or participation, as a basis for powerful human expression. …Read More
The ring shout is a spiritual expression in dance. It has its origins in a dance form, indigenous to much of Central and West Africa, in which the dancers move in a counterclockwise circle. …Read More
African American work songs originally developed in the era of slavery, between the seventeenth and nineteenth centuries. Because they were part of an almost entirely oral culture, they had no fixed form and only began …Read More

Fisk Jubilee Singers
African American (Negro) spirituals emerged from a mix of the brutal institution of slavery, Christian influences, and African culture. The songs expressed a yearning for a better life, claimed identification with the children of Israel, …Read More

The African influence in the blues is undeniable. The poetic structure and story-like verses carry on the oral tradition of West African cultures. Many African cultures made and performed on instruments similar to what …Read More

Boogie-woogie is a style of blues music, usually played on the piano, that is closely related to jazz forms such as ragtime and stride piano. As time went on, solo boogie-woogie extended from …Read More

Ragtime is a musical style that enjoyed its peak popularity between 1895 and 1918. Its cardinal trait is a syncopated or “ragged” rhythm.1 Sometimes referred to as “jig piano” or “piano thumping,” ragtime originated in …Read More

Dixieland, also known as hot jazz or traditional jazz, is a style of jazz developed in New Orleans at the start of the twentieth century. The rhythms and variations played in the city’s Congo Square …Read More

Swing is a style of jazz that, unlike Dixieland, features a larger-than-usual big band and a smoother beat, with flowing phrasing and less complex rhythms and harmonies than those featured in modern jazz.

Commonly referred to as stride, Harlem stride piano is a style of jazz piano that is a derivative form of Kansas City jazz and an extension of ragtime. According to historian Mervyn Cooke in his book Jazz, …Read More

Kansas City is world-renowned for its rich jazz and blues legacy. Blues formed the basic vocabulary for KC-style jazz. Blues singers of the 1920s and ragtime music greatly influenced the music scene, …Read More

Indigenous to Chicago, Illinois, Chicago blues is an electric blues style of urban blues. Urban blues evolved from classic blues following the Great Migration of African Americans, which was both forced and voluntary at times, …Read More

The calypso in Trinidad and Tobago is mainly of African origin and can be traced to the traditions of West Africa. The African traditions of call and response and ring shout are clearly present in calypso. …Read More


Many consider the birth of bebop in the 1940s the beginning of “modern” jazz. Bebop developed as the younger generation of jazz musicians expanded the creative possibilities of jazz beyond the dance-oriented swing style. …Read More

Rhythm and blues (R & B) was the most popular music created by and for African Americans between the end of World War II and the early 1960s. Georgia artists such as Ray Charles, Little Richard …Read More

Doo-wop is a subcategory that focuses on vocal jazz. This includes group harmony, a wide range of vocal parts, scat-like syllables, light or no instrumentation, and R & B rhythms and lyrics. The term doo-wop …Read More

Afro-Cuban jazz is the earliest form of Latin jazz. It mixes Afro-Cuban clave-based rhythms with jazz harmonies and techniques of improvisation. Afro-Cuban jazz emerged in New York City in 1947 with …Read More


Originally called “race music” because of its African American origins, rock and roll is a form of popular music that emerged in the United States in the late 1940s and early ’50s. Fats Domino was …Read More

A style of modern jazz that emerged in the US after World War II, cool jazz was created in contrast to the bebop movement and is more laid-back, featuring slow or moderate tempos and formal …Read More

Hard bop is an extension of bebop. The term “hard bop,” which emerged in the 1950s, was used to describe the new take on jazz that incorporated elements of rhythm and blues, gospel, and blues. …Read More

Bossa nova is a musical sub-genre derived from samba, with strong American jazz influences. Samba is a Brazilian music genre and dance style, with its roots in Africa (via the West African slave trade) …Read More

“Mainstream jazz” is a term established in the 1950s by music journalist Stanley Dance, who considered anything within the popular jazz music of the swing era “mainstream.” Another way to describe mainstream jazz is music …Read More

In a jazz context, an organ trio is a group of three jazz musicians, typically consisting of a Hammond organ player, a drummer, and either a jazz guitarist or a saxophone player. In some cases, …Read More

Soul music was partially the result of the urbanization and commercialization of rhythm and blues in the 1960s. Young black musicians, often nurtured in black churches, enjoyed and listened to …Read More

Free Jazz emerged during the late 1950s, reached its height in the ’60s, and has remained a major development in jazz since. There are no rules in Free Jazz. Musicians do not adhere to a fixed …Read More

Reggae is a genre that was strongly influenced by American jazz and R & B, especially the New Orleans R & B practiced by Fats Domino and Allen Toussaint. Reggae evolved out of the earlier genres ska and rocksteady. ..Read More

Ethno jazz, also known as world jazz, is a sub-genre developed internationally in the 1950s and ’60s broadly characterized by a combination of traditional jazz and non-Western musical elements.1 Jazz had become so popular …Read More

Jazz fusion is a musical genre that developed in the late 1960s when musicians combined jazz harmony and improvisation with funk, rock and roll, and R & B. The electric guitars, amplifiers, and keyboards that were popular …Read More

Funk is a music genre that originated in African American communities in the mid-1960s when African American musicians created a rhythmic, danceable new form of music through a mixture of soul, bebop/hard bop, and R & B. …Read More

In the early 1970s, Washington, D.C.-based musical pioneer Chuck Brown began laying the foundation for a new and innovative sound called go-go music. Driven by teenage musicians and audience members, the music was heavily …Read More

Said to be coined by Grandmaster Flash and the Furious Five member Keith “Cowboy” Wiggins, the music movement of hip-hop can be traced back to a “burnt out” South Bronx in New York City …Read More

Neo soul is a musical genre that fuses contemporary R & B and soul with elements of hip-hop, gospel, and jazz. Neo soul music is essentially modern-day soul music with contemporary attitudes and sensibilities. …Read More

Emerging in 2000, the musical convergence of hip-hop and jazz was inevitable. After all, early gospel, blues, and jazz employed call-and-response cadences dealing with the same themes prevalent in hip-hop: procreation, braggadocio, …Read More


Neo fusion is a term I am coining to describe what I believe to be a new genre of jazz emerging in the 2010s. I admit I’m out on a limb in the sense that …Read More